SRTM30 is a global bathymetry/topography data product distributed by the USGS EROS data center. The data product has a resolution of 30 seconds (roughly 1 km).
The code below is for python to directly download data from the noaa server (i.e. no need to download data through a browser). Below are relevant urls:
import urllib2
import StringIO
import csv
import numpy as np
import scipy.interpolate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
import pickle as pickle
# Definine the domain of interest
minlat = 42
maxlat = 45
minlon = -67
maxlon = -61.5
# Read data from: http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/usgsCeSrtm30v6.html
response = urllib2.urlopen('http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/usgsCeSrtm30v6.csv?topo[(' \
+str(maxlat)+'):1:('+str(minlat)+')][('+str(minlon)+'):1:('+str(maxlon)+')]')
data = StringIO.StringIO(response.read())
r = csv.DictReader(data,dialect=csv.Sniffer().sniff(data.read(1000)))
data.seek(0)
# Initialize variables
lat, lon, topo = [], [], []
# Loop to parse 'data' into our variables
# Note that the second row has the units (i.e. not numbers). Thus we implement a
# try/except instance to prevent the loop for breaking in the second row (ugly fix)
for row in r:
try:
lat.append(float(row['latitude']))
lon.append(float(row['longitude']))
topo.append(float(row['topo']))
except:
print 'Row '+str(row)+' is a bad...'
# Convert 'lists' into 'numpy arrays'
lat = np.array(lat, dtype='float')
lon = np.array(lon, dtype='float')
topo = np.array(topo, dtype='float')
# Data resolution determined from here:
# http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/info/usgsCeSrtm30v6/index.html
resolution = 0.008333333333333333
# Determine the number of grid points in the x and y directions
nx = complex(0,(max(lon)-min(lon))/resolution)
ny = complex(0,(max(lat)-min(lat))/resolution)
# Build 2 grids: One with lats and the other with lons
grid_x, grid_y = np.mgrid[min(lon):max(lon):nx,min(lat):max(lat):ny]
# Interpolate topo into a grid (x by y dimesions)
grid_z = scipy.interpolate.griddata((lon,lat),topo,(grid_x,grid_y),method='linear')
# Make an empty 'dictionary'... place the 3 grids in it.
TOPO = {}
TOPO['lats']=grid_y
TOPO['lons']=grid_x
TOPO['topo']=grid_z
# Save (i.e. pickle) the data for later use
# This saves the variable TOPO (with all its contents) into the file: topo.p
pickle.dump(TOPO, open('topo.p','wb'))
# Create map
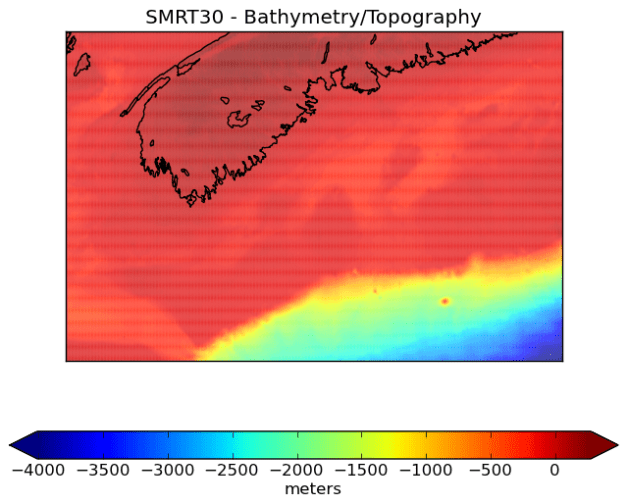
m = Basemap(projection='mill', llcrnrlat=minlat,urcrnrlat=maxlat,llcrnrlon=minlon, urcrnrlon=maxlon,resolution='h')
x,y = m(grid_x[1:],grid_y[1:])
fig1 = plt.figure()
cs = m.pcolor(x,y,grid_z,cmap=plt.cm.jet)
m.drawcoastlines()
m.drawmapboundary()
plt.title('SMRT30 - Bathymetry/Topography')
cbar = plt.colorbar(orientation='horizontal', extend='both')
cbar.ax.set_xlabel('meters')
# Save figure (without 'white' borders)
plt.savefig('topo.png', bbox_inches='tight')

for me it worked changing this line…
cbar = plt.colorbar(cs, orientation=’horizontal’, extend=’both’)
Thanks a lot
Since this is gridded data, using CSV as output and then using interpolate is a lot of extra work. ERDDAP supports many gridded file format output as well, and since you want to access this data later, NetCDF is a great option. You can do this by just using the extension ‘.nc’ on the ERDDAP request. Here’s an example IPython Notebook: http://nbviewer.ipython.org/gist/rsignell-usgs/a4f418c3f588ca32e116
I have the following problem, how can I solve it?
File “C:/Users/…”, line 27, in
data = io.StringIO(response.read())
TypeError: initial_value must be str or None, not bytes